
Dynamické DNS
Centrum podpory
Ke stažení
Frequently Asked Question
DnsUp první Dynamické DNS služby s jasnou Evropskou konotace přístupné po celém světě.
DnsUp nabízí bezplatné a placené řešení a je zaměřena na všechny uživatele, kteří potřebují, aby jejich služeb vždy po ruce.
DnsUp nabízí bezplatné a placené řešení a je zaměřena na všechny uživatele, kteří potřebují, aby jejich služeb vždy po ruce.
Na DNS (Domain Name Systém) je systém, který umožňuje dvojici jméno s adresou IP. Ve skutečnosti, stroje lépe pracovat s čísly a tedy identifikovat se používají ip adresy (ex: 216.58.205.174), zatímco lidé si pamatují lepší jména (es: google.com) .
Když zadáte "google.com" nebo "www.google.com" na adresním řádku prohlížeče, Internet architektura je taková, že příslušný DNS server je kontaktován a výnosy přiřazené IP adresy (216.58. 205.174 v tomto případě). Přes tuto adresu, prohlížeč je schopen jednoznačně rozpoznat server, který spravuje Google, word wide web, služby a načíst požadovanou stránku, konkrétně ten, vztahující se k vyhledávání motor.
Když zadáte "google.com" nebo "www.google.com" na adresním řádku prohlížeče, Internet architektura je taková, že příslušný DNS server je kontaktován a výnosy přiřazené IP adresy (216.58. 205.174 v tomto případě). Přes tuto adresu, prohlížeč je schopen jednoznačně rozpoznat server, který spravuje Google, word wide web, služby a načíst požadovanou stránku, konkrétně ten, vztahující se k vyhledávání motor.
Když Internet byl vynalezen nebyl si myslel, že by se stala tak všudypřítomná. Původně tam bylo několik desítek počítačů připojených k sobě navzájem a každý z nich byl identifikován podle ip adresy (stejný ten, který používáme dnes). Při současném systému je možné vytvořit 4 miliardy různých IP adres, to znamená 4 miliard zařízení připojených k Internetu ve stejnou dobu, cíl, který byl myšlenka být nedosažitelné.
V průběhu let, počet uživatelů roste neuvěřitelnou rychlostí a byl to již není možné staticky přiřadit adresy ip pro každé připojení. Bylo to proto, že k přiřazení ip adresy k potřebě, která je dynamicky.
Každý poskytovatel služeb internetu (isp) má omezený počet ip adres, které přiděluje k uživateli náhodně, když se to připojí a to může v průběhu času měnit , i když připojení zůstává.
Tímto způsobem uživatel je schopen získat přístup k internetu bez nutnosti jedinečnou identitu (IP adresu), ale to není problém ve většině případů, a často to je chování, které není vnímáno.
V průběhu let, počet uživatelů roste neuvěřitelnou rychlostí a byl to již není možné staticky přiřadit adresy ip pro každé připojení. Bylo to proto, že k přiřazení ip adresy k potřebě, která je dynamicky.
Každý poskytovatel služeb internetu (isp) má omezený počet ip adres, které přiděluje k uživateli náhodně, když se to připojí a to může v průběhu času měnit , i když připojení zůstává.
Tímto způsobem uživatel je schopen získat přístup k internetu bez nutnosti jedinečnou identitu (IP adresu), ale to není problém ve většině případů, a často to je chování, které není vnímáno.
Jakmile pochopíte, co je DNS a jak IP adresy jsou přiřazeny to je snadné pochopit roli Dynamické DNS.
Na Dynamické DNS je systém, který udržuje asociace mezi jménem (např: hostitel.dnup.eu) a stroj (server nebo router) pomocí aktualizace IP adresu na čas, který se mění v čase.
Pojďme se podívat, jednoduchý příběh uživatele:
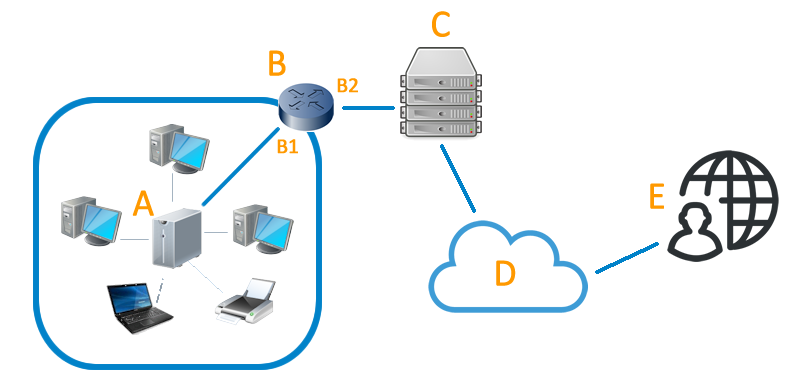
Na NAS server (A) v místní síti přístup k internetu (D) prostřednictvím služby poskytovatele (C).
Na routeru (B) má dvě adresy: soukromé (B1), vybrán správce LAN a veřejné (B2) přidělena dynamicky (C).
Na předmět (E), majitel LAN, chce kontaktovat server k načtení dokumentu, ale k tomu musí znát adresu (B2), která je dynamická, mění s určitou frekvencí.
Naštěstí (E) má předplatné dnsUp které díky aktualizaci klienta zná veřejnou adresu B2 a udržuje aktualizovaný přidružení mezi hostitele hostitel.dnup.eu a routeru (B).
Tímto způsobem (E), pro přístup k NAS serveru () a všechny jeho služby, musí prostě vzpomenout na jméno "myhost.dnup.eu", který byl nakonfigurován na dnsUp.
Na Dynamické DNS je systém, který udržuje asociace mezi jménem (např: hostitel.dnup.eu) a stroj (server nebo router) pomocí aktualizace IP adresu na čas, který se mění v čase.
Pojďme se podívat, jednoduchý příběh uživatele:

Na NAS server (A) v místní síti přístup k internetu (D) prostřednictvím služby poskytovatele (C).
Na routeru (B) má dvě adresy: soukromé (B1), vybrán správce LAN a veřejné (B2) přidělena dynamicky (C).
Na předmět (E), majitel LAN, chce kontaktovat server k načtení dokumentu, ale k tomu musí znát adresu (B2), která je dynamická, mění s určitou frekvencí.
Naštěstí (E) má předplatné dnsUp které díky aktualizaci klienta zná veřejnou adresu B2 a udržuje aktualizovaný přidružení mezi hostitele hostitel.dnup.eu a routeru (B).
Tímto způsobem (E), pro přístup k NAS serveru () a všechny jeho služby, musí prostě vzpomenout na jméno "myhost.dnup.eu", který byl nakonfigurován na dnsUp.
Dynamic DNS se používá k mít své služby vždy po ruce. Služby, které místní síť může poskytnout více, například:
- NAS server pro centralizovanou správu dokumentů,
- Kamery pro ostrahu objektu
- Privátní cloud server, například Nextcloud
- Peer-to-peer služby pro sdílení dat
- DLNA server pro distribuci multimediálního obsahu
- Přizpůsobené služby pro firemní mobilní zařízení,
Adresa je textový řetězec, který identifikuje zdroj. Například:
http://www.dnsup.eu
doména je část, která navazuje na typ protokolu (http, v tomto případě) a je interpretován zprava doleva. Proto máme:
V podstatě domény zahrnuje první a druhý stupeň (dnsup.eu) a to je dost k vytvoření asociací mezi jménem a ip adresu.
Dynamické DNS služby vám umožní svobodně si vybrat doménu třetí úrovně, přičemž všechny tyto mohou být vybrány ze seznamu, nebo vybrat (v závislosti na typu předplatného).
Mezi možné domén dnsUp nabízí dd1.biz, s níž si můžete sestavit svou vlastní doménu, takže například hostitel.dd1.biz je platnou volbou.
Pojďme se podívat, co různé plány nabídka:
http://www.dnsup.eu
doména je část, která navazuje na typ protokolu (http, v tomto případě) a je interpretován zprava doleva. Proto máme:
- top-level domain, eu (Evropa) a to musí být vybrán ze širokého seznamu, ale v žádném případě ne modifikovatelné (není-li příslušnými orgány)
- domény druhé úrovně, dnsup , který může být volně složené
- třetí úrovně domény, není nutné, ale často se používá k určení typu nabízených služeb (například www znamená, že world wide web, ale to je jen konvence)
V podstatě domény zahrnuje první a druhý stupeň (dnsup.eu) a to je dost k vytvoření asociací mezi jménem a ip adresu.
Dynamické DNS služby vám umožní svobodně si vybrat doménu třetí úrovně, přičemž všechny tyto mohou být vybrány ze seznamu, nebo vybrat (v závislosti na typu předplatného).
Mezi možné domén dnsUp nabízí dd1.biz, s níž si můžete sestavit svou vlastní doménu, takže například hostitel.dd1.biz je platnou volbou.
Pojďme se podívat, co různé plány nabídka:
- Zdarma: tento plán je k dispozici zdarma na test bez časového omezení, kvalitu služby. V tomto případě je k dispozici domény je dd0.eu
- Posílena: v tomto případě dvě domény jsou k dispozici, dd0.eu a dd1.biz
- Plus: tento plán nabízí stejné domény, které najdeme v Rozšířené a kromě toho můžete uvést doménu vaší volbou pro každého předplatného
- se Podařilo: podařilo plán poskytuje domény uvedené uživatelem
